All through the lifetime of a mission, mission managers verify in on progress and evaluate it to the mission plan—evaluating their predictions to actuality. In the event that they don’t do that repeatedly, odds are the finances will undergo and their mission will fail. Fortunately, these deviances from the plan, comparable to price variance, don’t should sink a mission.
In actual fact, they will strengthen it. The secret is recognizing them and making changes to remain on the best path. Among the finest methods to keep away from price overrun is by calculating price variance.
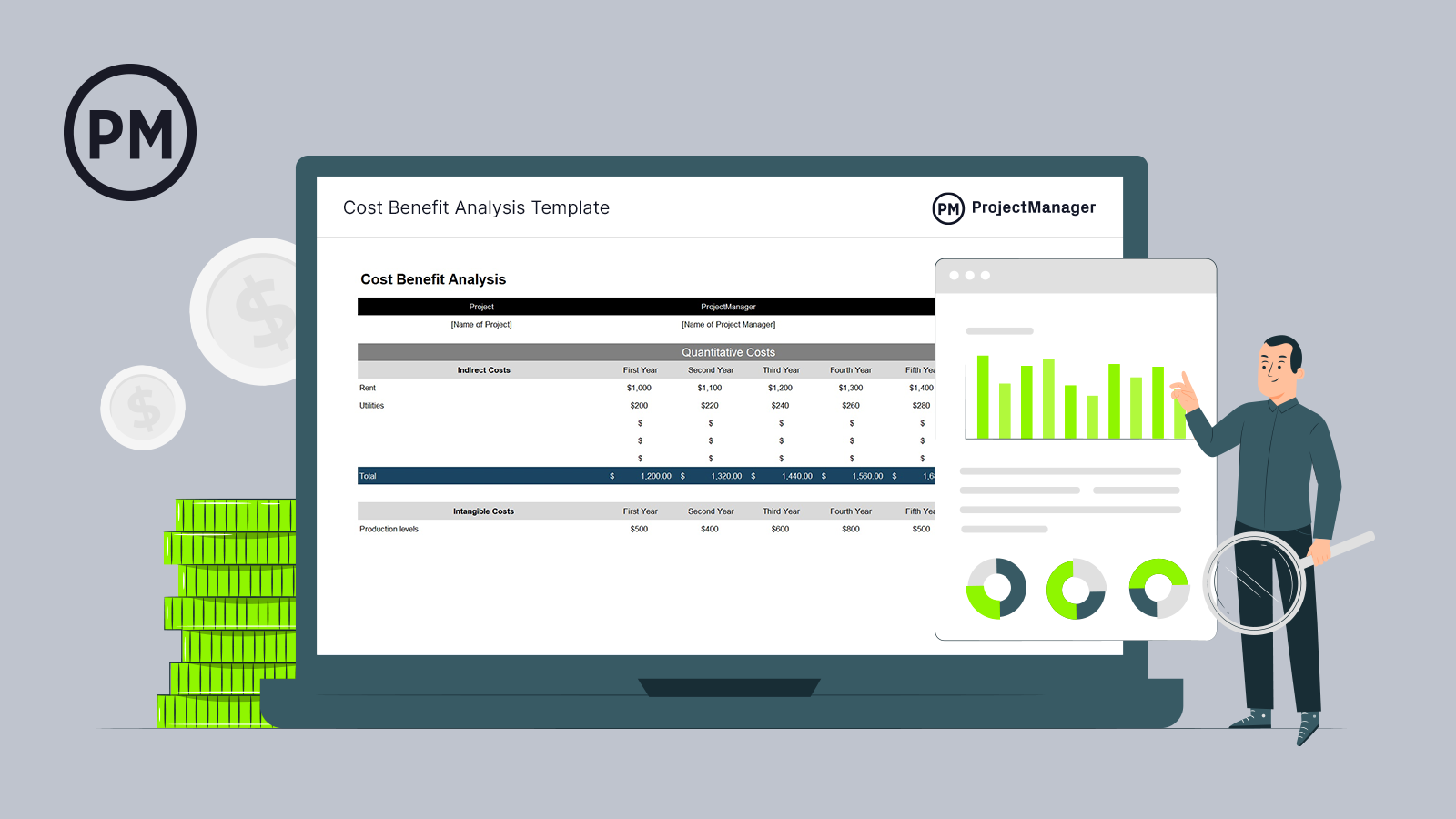

Get your free
Value Profit Evaluation Template
Use this free Value Profit Evaluation Template for Excel to handle your initiatives higher.
What Is Value Variance in Undertaking Administration?
Value variance (additionally known as CV) is the distinction between mission prices estimated in the course of the planning part and the precise prices. In different phrases, it’s how a lot precise prices differ from budgeted prices. Calculating price variance is how mission managers monitor bills to see if a mission is below or over finances.
These calculations are a part of a method known as earned worth administration (EVM). In an EVM system, the objective of price administration is to ascertain whether or not a variance is constructive, unfavorable or zero.
When mission managers have this earned worth evaluation info, they will make the required changes to remain on monitor. If a variance is extraordinarily excessive (unfavorable), adjustments have to be made. If there’s a particularly low-cost variance (constructive) or zero variance, they will take it as an indication of efficient price administration.
Constructive Value Variance vs. Damaging Value Variance
Value variance (CV) is a key efficiency metric in mission administration that measures the distinction between the budgeted price of labor carried out (earned worth) and the precise price incurred. It helps mission managers assess whether or not a mission is below or over finances.
Constructive price variance signifies that the mission is below finances. This occurs when the earned worth is bigger than the precise price. For instance, in case your mission has earned $50,000 price of labor however you’ve solely spent $45,000, your price variance is +$5,000. A constructive CV suggests environment friendly price administration and useful resource use.
Damaging price variance means the mission is over finances. This happens when the precise price exceeds the earned worth. As an example, in case you’ve accomplished $40,000 price of labor however spent $45,000, your price variance is -$5,000. A unfavorable CV flags potential points comparable to scope creep, underestimation, or misallocated assets, and normally requires corrective motion.
Understanding and monitoring price variance is essential for sustaining monetary management and making certain mission profitability.
The right way to Calculate Value Variance in Undertaking Administration
Value variance is precisely how a lot a mission is over or below finances. That is calculated utilizing the associated fee variance method.
Value Variance Method
Within the earned worth administration (EVM) methodology utilized in mission administration, price variance (CV) measures the distinction between the worth of labor carried out and the precise price incurred.
It’s calculated utilizing the method under, the place EV stands for earned worth and AC is precise price. A constructive CV signifies below finances; a unfavorable CV indicators price overruns.
Value Variance (CV) = Earned Worth (EV) – Precise Value (AC)
- Precise Value (AC): The full price incurred for work carried out on a mission as much as a selected level. It contains all direct and oblique bills, comparable to labor, supplies, and tools, whatever the mission’s progress.
- Earned Worth (EV): The budgeted worth of the work really accomplished at a given time limit. It displays mission progress in financial phrases and is used to match deliberate versus precise efficiency.
Value Variance Calculation Strategies
Value variance calculation strategies are methods used to measure the distinction between a mission’s deliberate and precise prices at varied closing dates.
There are three most important price variance calculation strategies, cumulative price variance technique, period-by-period price variance technique and variance at completion technique.
These three strategies apply the associated fee variance method (CV = EV – AC) at totally different phases of the mission.
Cumulative Value Variance Technique
The cumulative price variance (CV) technique calculates the distinction between the earned worth (EV) and precise price (AC) of a mission as much as a selected time limit. It displays the general price efficiency throughout all the mission period thus far.
Method: CV = EV – AC
This technique supplies a high-level overview of whether or not the mission is below or over finances, making it helpful for ongoing finances monitoring and pattern evaluation. It helps stakeholders assess long-term mission efficiency moderately than remoted price points.
Interval-by-Interval Value Variance Technique
The period-by-period price variance technique focuses on brief time intervals—usually weekly or month-to-month—calculating the associated fee variance for every particular interval.
Method (per interval): CV = EV (for the interval) – AC (for the interval)
This technique permits mission managers to pinpoint when price deviations happen, providing a extra detailed and fast perception into spending points. It’s best for figuring out short-term tendencies or sudden spikes in prices that won’t but be mirrored in cumulative knowledge.
Variance at Completion (VAC) Technique
Variance at completion (VAC) forecasts the anticipated price variance on the finish of the mission. It compares the whole mission finances, often known as the finances at completion (BAC), with the forecasted price, or estimate at completion (EAC).
Method: VAC = BAC – EAC
This technique helps mission managers anticipate whether or not they’re more likely to full the mission below or over finances, enabling higher long-term monetary planning and corrective motion earlier than mission closure.
What Are the Important Causes of Value Variance In Undertaking Administration?
Value variance in mission administration refers back to the distinction between the estimated price and the precise price of a mission. Whereas small variances are anticipated, vital variations usually sign deeper points that may have an effect on mission success. Understanding the foundation causes of price variance is crucial for controlling budgets, managing expectations and delivering worth.
Inaccurate Value Estimates
Poor preliminary price estimates can derail a mission’s monetary trajectory from the beginning. This normally happens when estimates are primarily based on incomplete knowledge, guesswork, or overly optimistic assumptions. With out thorough analysis and skilled enter, finances baselines might not replicate the true scope or complexity of the work.
Scope Creep
When new options, duties or deliverables are added to a mission with out corresponding finances changes, it results in scope creep. This usually outcomes from unclear necessities or lack of change management processes. The extra the scope expands, the extra prices rise—usually unexpectedly.
Schedule Delays
Delays in mission timelines can considerably enhance prices as a result of prolonged useful resource use, contract penalties or the necessity to speed up later work phases. Time-sensitive prices like tools leases or employees salaries usually grow to be inflated when a mission runs not on time.
Useful resource Value Fluctuations
The value of labor, supplies and subcontractor providers can change as a result of market situations, availability or exterior financial components. If a finances doesn’t account for potential value shifts or inflation, it may possibly trigger substantial price overruns.
Undertaking Dangers
Sudden occasions comparable to regulatory adjustments, climate delays or technical points can disrupt progress and incur further prices. And not using a strong threat administration plan, initiatives might wrestle to soak up the monetary influence of such occasions.
Low Productiveness or Useful resource Utilization Inefficiency
When groups aren’t working effectively—as a result of poor coaching, unclear route or lack of coordination—mission duties take longer and require extra assets. Inefficient useful resource utilization drives up labor prices and impacts total price efficiency.
Value Variance Evaluation Examples
To raised perceive the idea of price variance evaluation we’ve created an instance in a few totally different industries. This could assist to indicate how the method works in a real-life state of affairs.
Building Value Variance Evaluation Instance
This price variance evaluation instance is for the development trade. Right here, the mission is engaged on the muse of an workplace constructing.
Undertaking: Workplace Constructing Building
Process: Basis Work
- Deliberate Worth (PV): $80,000
- Earned Worth (EV): $75,000
- Precise Value (AC): $90,000
CV = $75,000 – $90,000 = –$15,000
Evaluation: The inspiration work is $15,000 over finances. Though 75 p.c of the work has been accomplished (EV), precise spending exceeded expectations as a result of unexpected soil stabilization points and higher-than-estimated concrete prices. This unfavorable variance highlights a must revise price estimates for future phases and assess vendor pricing accuracy.
Manufacturing Value Variance Evaluation Instance
On this price variance evaluation instance, we’re coping with a producing firm. They’ve a run of metal frames that require welding and meeting.
Undertaking: Manufacturing of 500 Metal Frames
Process: Welding and Meeting
- Deliberate Worth (PV): $60,000
- Earned Worth (EV): $55,000
- Precise Value (AC): $50,000
Value Variance (CV) = EV – AC
CV = $55,000 – $50,000 = +$5,000
Evaluation: The welding and meeting activity is $5,000 below finances. Though solely 92 p.c of the deliberate work has been accomplished, the precise price got here in decrease as a result of greater labor effectivity and a bulk low cost on welding provides. This favorable variance suggests sturdy manufacturing efficiency and potential to reallocate financial savings to later phases.
Understanding Undertaking Prices
All initiatives price cash, no matter their dimension, scope or deliverables. We’ve all heard “there’s no such factor as a free lunch.” The identical goes for initiatives – there’s no such factor as a mission with out prices. These prices are available in many alternative kinds, from the price of supplies to easily the price of doing enterprise (lease, salaries, and many others.). It’s the mission supervisor’s job to take all of those prices under consideration and create a versatile finances.
Undertaking prices, regardless of the kind, have to be correctly managed and tracked all through the life cycle of a mission. If mission managers don’t preserve a detailed eye on the mission, it may be detrimental to the mission’s success. Plus, having real-time knowledge entry is crucial to serving to mission managers make changes.
Undertaking administration software program is foundational in planning and monitoring mission prices. ProjectManager is award-winning mission administration software program that has the resource-focused instruments you could evaluate your deliberate and precise prices in actual time. Use our in-depth Gantt chart to set a baseline when you’ve scheduled your duties, prices and assets. Use it to know your mission prices at a look and make changes as wanted in actual time.

Totally different Sorts of Undertaking Prices
To completely perceive mission price variance, it’s useful to be acquainted with the primary kinds of mission prices. Check out the 4 you’re most probably to see. Most initiatives have all 4, and every can contribute to total price variance:
- Direct Prices: Consider direct prices as prices that go straight to the mission to attain deliverables. A useful instance of a direct price is the price of the fabric wanted to construct one thing. The price of these supplies goes towards creating an finish product.
- Oblique Prices: Oblique prices, alternatively, go towards funding “behind the scenes” bills incurred all through the lifetime of a mission. They’re also referred to as overhead prices. For instance, the price of renting an workplace area is a standard expense fastened overhead. This expense should be paid to finish the mission, nevertheless it additionally goes towards supporting different initiatives.
- Fastened Prices: Fastened prices are bills with set costs that aren’t topic to any form of change. These are reliable prices that won’t fluctuate and probably throw off a finances. Each direct and oblique prices may also be fastened prices (or variable prices). A hard and fast price, for instance, may seem like the flat charge a contractor fees for his or her providers.
- Variable Prices: Variable prices, alternatively, will not be as predictable. For instance, the price of tools rental might go up or down relying on the seller, the demand or how lengthy the tools is required.
- Overhead Prices: Overhead prices are oblique bills required to run a mission or enterprise, comparable to utilities, lease, and administrative salaries. They help operations however aren’t tied to particular deliverables or duties.
Associated: Free Undertaking Funds Template for Excel
Different Sorts of Value Variance In Undertaking Administration and Value Accounting
In addition to the associated fee variance method that’s utilized in earned worth administration, there are different kinds of price variance which can be utilized in mission administration and price accounting, particularly in manufacturing and building initiatives.
Materials Value Variance (MCV)
Materials price variance (MCV) is a key metric in price accounting and mission administration used to measure the distinction between the anticipated price of supplies (primarily based on customary prices) and the precise price incurred.
MCV is most helpful in manufacturing and building initiatives the place materials bills make up a good portion of the whole price. It helps managers establish pricing points, provider efficiency issues, procurement inefficiencies or market-driven price adjustments.
Materials Value Variance Method
MCV = (SQ × SP) – (AQ × AP)
- SQ= Customary Amount
- SP= Customary Value
- AQ= Precise Amount
- AP= Precise Value
Labor Value Variance (LCV)
Labor price variance (LCV) is a mission and price administration metric that measures the distinction between the usual price of labor and the precise labor price incurred throughout a mission or manufacturing cycle.
LCV is particularly vital in labor-intensive industries comparable to building, manufacturing, and service-based initiatives. It’s used to observe effectivity, wage fee fluctuations and workforce productiveness.
Labor Value Variance Method
LCV = (SH × SR) – (AH × AR)
- SH= Customary Hours
- SR= Customary Price
- AH= Precise Hours
- AR= Precise Price
Overhead Value Variance
Overhead price variance is a monetary metric used to evaluate the distinction between the budgeted (or customary) overhead prices and the precise overhead prices incurred throughout a mission or manufacturing interval.
This metric is especially helpful in environments with fastened budgets and recurring oblique prices, comparable to in manufacturing vegetation or large-scale infrastructure initiatives. Overhead price variance helps managers perceive how effectively they’re controlling oblique spending and may spotlight inefficiencies like underutilized amenities, inaccurate price allocation strategies, or surprising will increase in overhead bills.
Variable Overhead Variance Method
VOHV = (SH × SR) – (AH × AR)
- SH= Customary Hours
- SR= Customary Price
- AH= Precise Hours
- AR= Precise Price
Fastened Overhead Variance Method
FOHV = Budgeted Fastened Overhead – Precise Fastened Overhead
Different Value Variance Evaluation Formulation Utilized in EVM
Whereas the method defined above is the primary one used to calculate price variance in mission administration, there are different earned worth administration (EVM) formulation that may assist with price variance evaluation.
Value Efficiency Index Method
Value Efficiency Index (CPI) = Earned Worth (EV) / Precise Value (AC)
A value efficiency index (CPI) is a metric used to guage how effectively assets are being utilized in a mission. When fixing for a CPI, the worth will probably be one in every of two issues:
Lower than or equal to 1 (assets will not be getting used effectively)
Better than or equal to 1 (assets are getting used effectively)
To resolve for CPI, you have to divide the earned worth by precise prices.
To Full Value Efficiency Index Method
To Full Value Efficiency Index (TCPI) = (Complete Funds – EV) / (Complete Funds – AC)
Fixing for an entire price efficiency index (TCPI) is extraordinarily useful, particularly in case you’re experiencing a excessive (unfavorable) mission price variance. A TCPI is an index that exhibits how assets should be used for the remainder of a mission to return in below or on finances.
To seek out your TCPI, start by subtracting your earned worth out of your complete finances. Then, subtract your precise price from the whole finances. Final, divide the primary quotient by the second quotient.
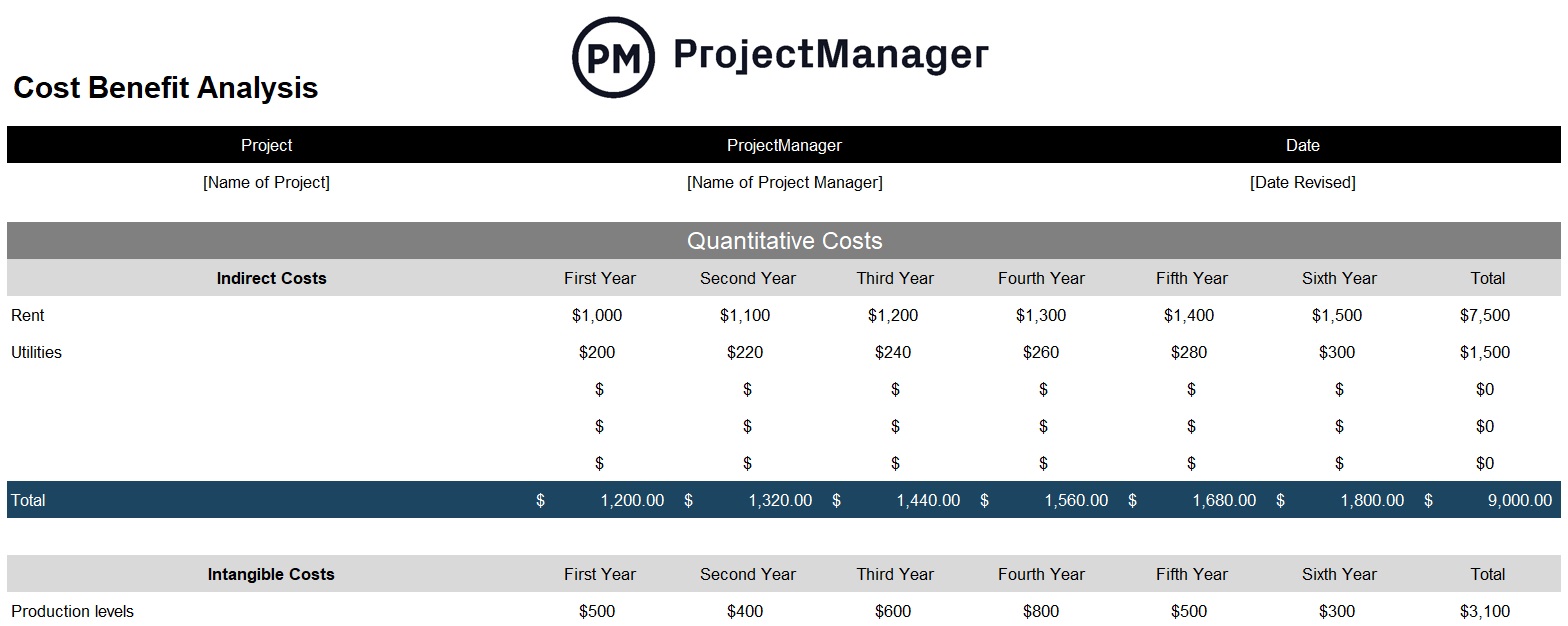
Free Value Profit Evaluation Template
Earlier than price variance comes into play, you could decide if the mission bills are justified. Obtain our free cost-benefit evaluation template for Excel to shortly crunch the numbers and decide if the mission is sensible from a value perspective. Entry to this knowledge makes it simple for mission managers to find out if a mission will probably be profitable.

How ProjectManager Helps Calculate Value Variance in Actual Time
All through the lifetime of a mission, you’ll need to have every of those price variance formulation at your disposal. Fortunately, there are price administration instruments that make holding your eye on variances easy so that you just don’t should manually crunch the numbers.
ProjectManager fills formulation with the proper values robotically and prevents any human error that may result in main budgeting errors. Components like complete finances, precise prices, earned values and extra are up to date in real-time so that you just’re all the time seeing probably the most present knowledge.
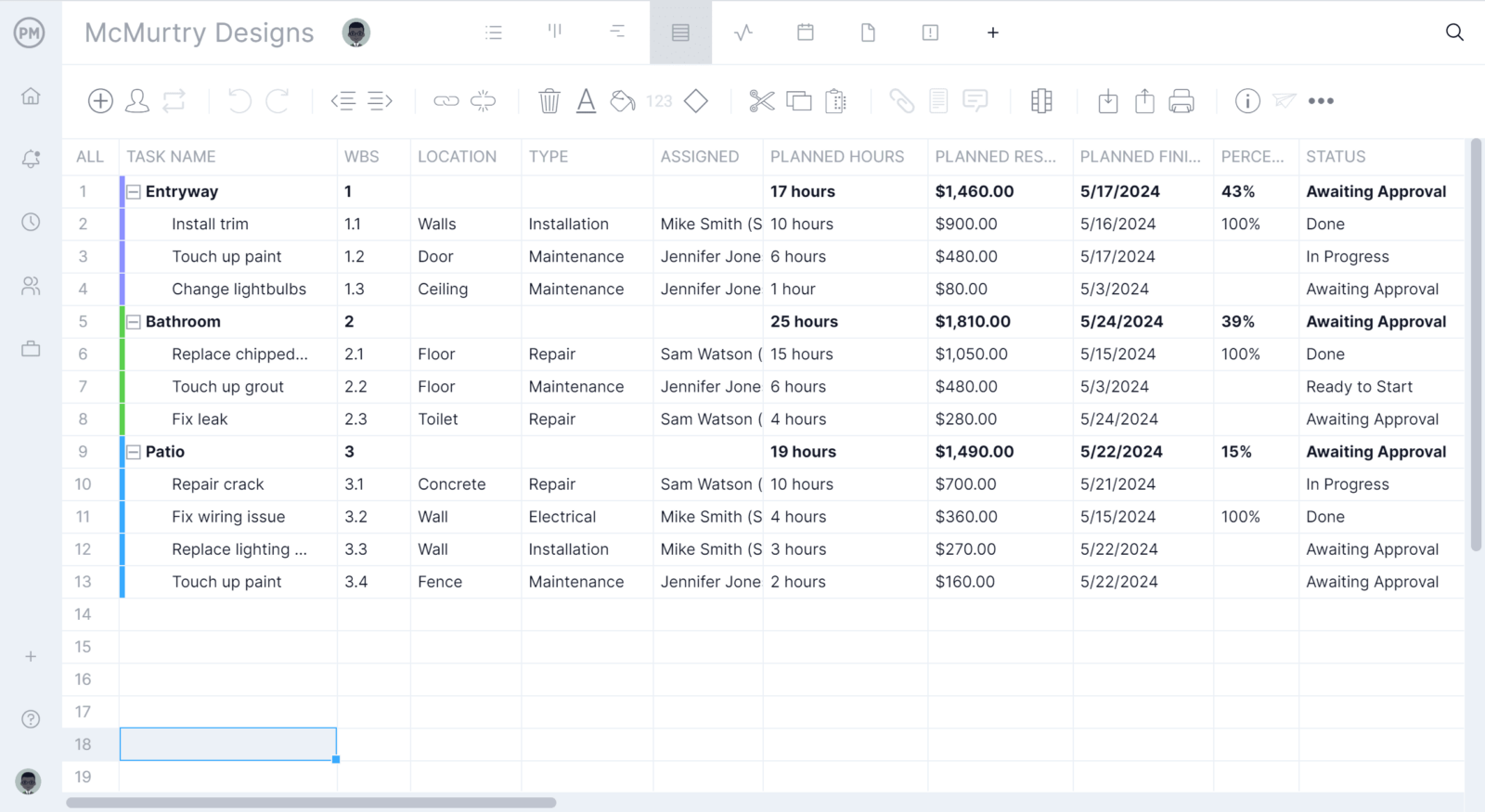

Create and handle mission budgets, in addition to see how precise prices evaluate to deliberate prices on the mission dashboard. The ProjectManager mission dashboard updates robotically, so that you’re all the time trying on the most present figures and make the neatest budgeting selections. This makes all of the distinction between recognizing price variances and lacking essential particulars. Preserve your eye on price baselines, in addition to spending and the place initiatives are at when it comes to finances.
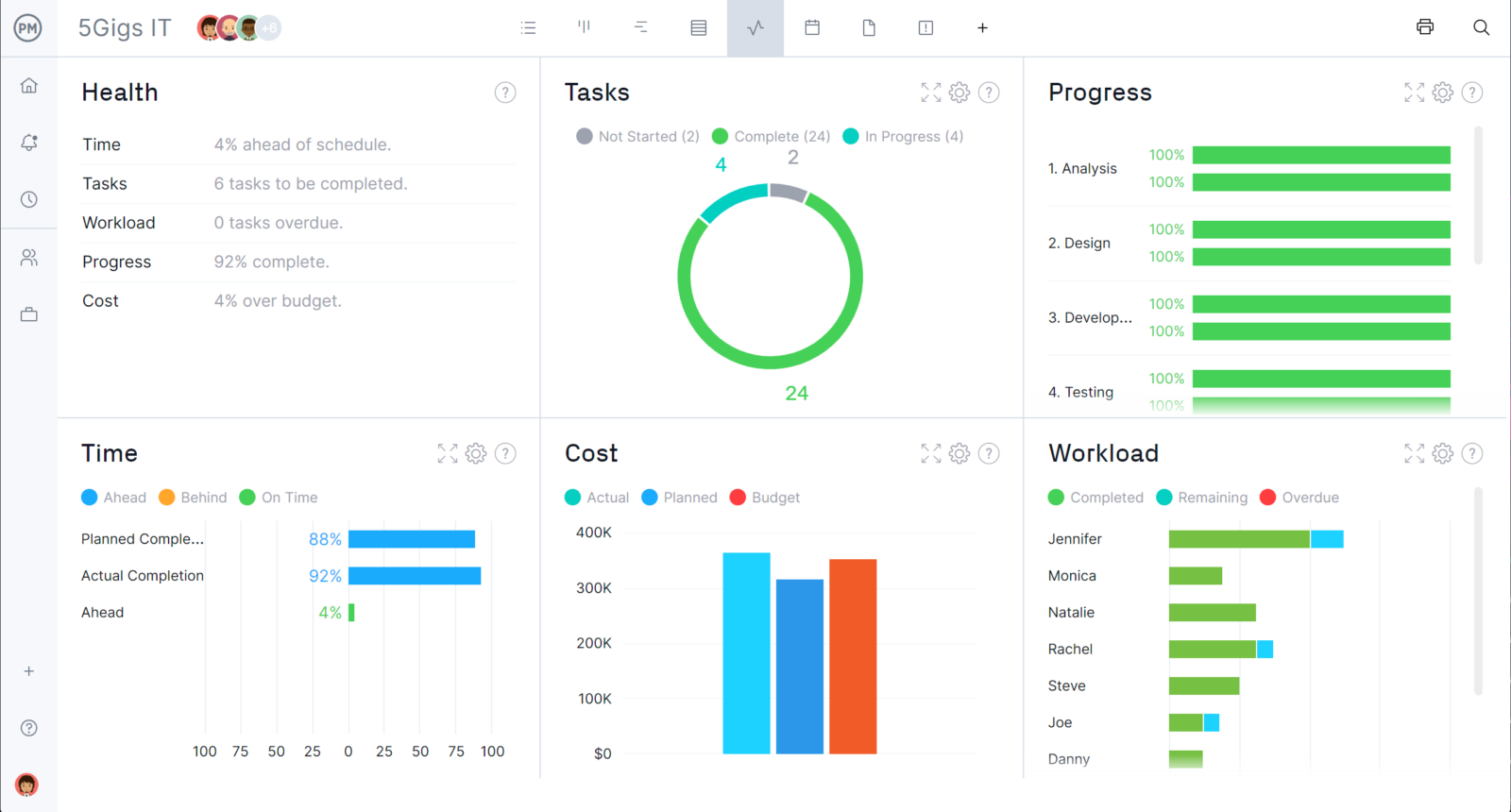

Must share this info with stakeholders? Create a finances report in only some clicks to maintain the crew on top of things and making the most effective selections collectively. Having this info at your fingertips and having the ability to share it’s the distinction between initiatives staying on finances and going over finances, which may end up in price overrun and complete failure.

Calculating price variance requires mission administration software program strong sufficient to calculate and arrange your knowledge in actual time. ProjectManager is on-line mission administration software program that retains your mission’s prices inside finances. Attempt it in the present day with this free 30-day trial.







